Lightweight FRP Structures: Enhancing Sustainability and Performance Across Industries

Lightweight fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP) are revolutionizing industries that have long relied on traditional materials to provide structural strength and durability. The construction, transport, and automotive industries are using FRP composites to reduce weight which helps improve fuel efficiency and optimize performance.
The most popular method of lightweighting is swapping out heavier components and materials for ones that are less dense and/or stronger. At a quarter the weight of steel and lighter than aluminum, glass fiber-reinforced plastics (GFRP) are being used by engineers and designers to develop components that are lighter, stronger, and more sustainable.
While the exceptional properties of carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) justifies its high price tag for use in sports cars, aerospace, and competitive yachts – it is not economically viable for most construction projects.
GFRP composites are lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making them an ideal material for a range of applications. They are composed of a polymer matrix, typically epoxy, vinylester, or polyester; and reinforced with glass fibers, which provide the necessary strength and stiffness. By using GFRP composites, manufacturers can create lightweight yet robust components that are more energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.
GFRP, CFRP, and Steel: Comparing Weight, Strength and Cost
GFRP (glass fiber-reinforced plastic) and CFRP (carbon fiber-reinforced plastic) are both composite materials that are used as alternatives to traditional steel in various applications. Here is a comparison of the weight, cost, and strength of these materials:
Weight:
- GFRP is a lightweight material, weighing only 25% of the density of steel.
- CFRP is approximately 10% lighter than GFRP.
Cost:
- GFRP is low-cost and price competitive with steel for many applications.
- CFRP is the most expensive of the three materials. While the exceptional properties of CFRP justifies its high price tag for use in sports cars, aerospace, and competitive yachts – it is not a viable economic option for most construction projects.
Strength:
- Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it a popular material for construction and engineering applications. Its strength is compromised when exposed to corrosive environments so rigorous maintenance programs and/or cathodic protection are often required.
- GFRP has a high strength-to-weight ratio, it is twice the tensile strength of steel and it is corrosion-resistant. It is now widely used to reinforce concrete in bridges, seawalls, and water treatment plants. Other infrastructure solutions include bolts, anchors, and dowels which can be viewed in our Composite Solutions Infrastructure brochure.
- CFRP has an even higher strength-to-weight ratio than GFRP and has a higher modulus, which makes it suitable for aerospace.
The choice of material depends on the specific application and the desired properties. Steel is often used for its strength and durability, whereas GFRP and CFRP are also lightweight and resistant to corrosion. Whatever materials are selected, it is always the goal to achieve the best performance and cost outcomes for the application with material weight often being an important deciding factor.
GFRP Composites are Lighter for EVs, Construction, and Snowmobiles
EVs, bridges, and snowmobiles – these three applications show the benefits of replacing conventional materials with a lighter GFRP composite:
Lightweight GFRP Components for Energy-Efficient EVs
The race is on in the automotive industry to reduce electric vehicle (EV) weight. The use of GFRP and CFRP composites in the automotive industry has gained popularity due to their low weight and high strength. The weight reduction of EVs is crucial to their efficiency and range, which is why GFRP pultruded composites are increasingly used.
A recent example of lightweighting using pultrusion, is the latest seat design for the Toyota Tundra EV. A GFRP pultruded beam was used to achieve the strength and stiffness required for the seat frame. The GFRP beam has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than high-carbon steel making it the ultimate solution. The efficiency of producing the pultruded composite is added to the cost savings which makes for a competitive price point for the end user.

Toyota and other automakers use a combination of CFRP and GFRP pultrusion to make their EVs lighter.
FRP Bridge Construction
The construction industry used a range of GFRP composites in the form of concrete reinforcement, form ties, and bolts for tunnels. GFRP composites offer several benefits in construction including being corrosion-resistant, highly durable, and delivering long life cycles with little maintenance.
One of the exciting benefits of lightweight GFRP construction products is the savings achieved across the whole life cycle of a project:
- At ¼ the weight of steel, GFRP rebar is more economical and fuel-efficient to transport to the construction site.
- Heavy lifting equipment is often not required.
- Faster installation means less labor.
- Reduced worker fatigue and injury.
- GFRP rebar requires less concrete coverage which not only makes the project lighter, it also saves concrete.
Harkers Island Bridge in North Carolina (pictured above) is the world's largest bridge to date, without steel reinforcement. The North Carolina Department of Transport selected Mateenbar™ Fiberglas™ Rebar was selected to construct a durable and corrosion-resistant bridge.
GFRP Structural Support for Snowmobile Track
GFRP composites have been used to reduce the weight of the vehicle while maintaining its strength and durability. Lightweight snowmobiles provide better fuel efficiency and improved handling, making them an attractive option for enthusiasts.
The GFRP pultruded rod used to provide structural support to the track can bend and flex back into shape when traveling over rough terrain. It is lighter than steel, which reduces the fuel consumption of the snowmobile.
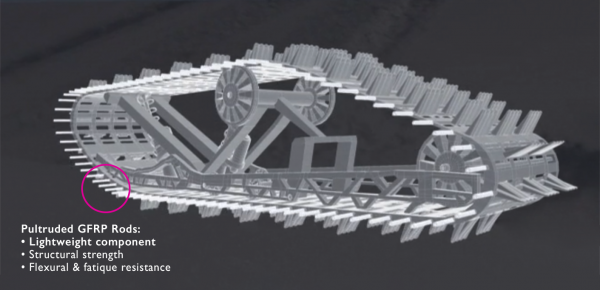
Pultruded FRP structural support profile in a snowmobile track.
Lightweight GFRP materials are Durable and Sustainable
The environment and sustainability are more important to consumers than ever. Shifting to sustainable materials, that are lightweight results in energy efficiency, improved performance, and reduced carbon footprint. As the demand for lightweight continues to increase, it is likely that GFRP composites will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of various industries.